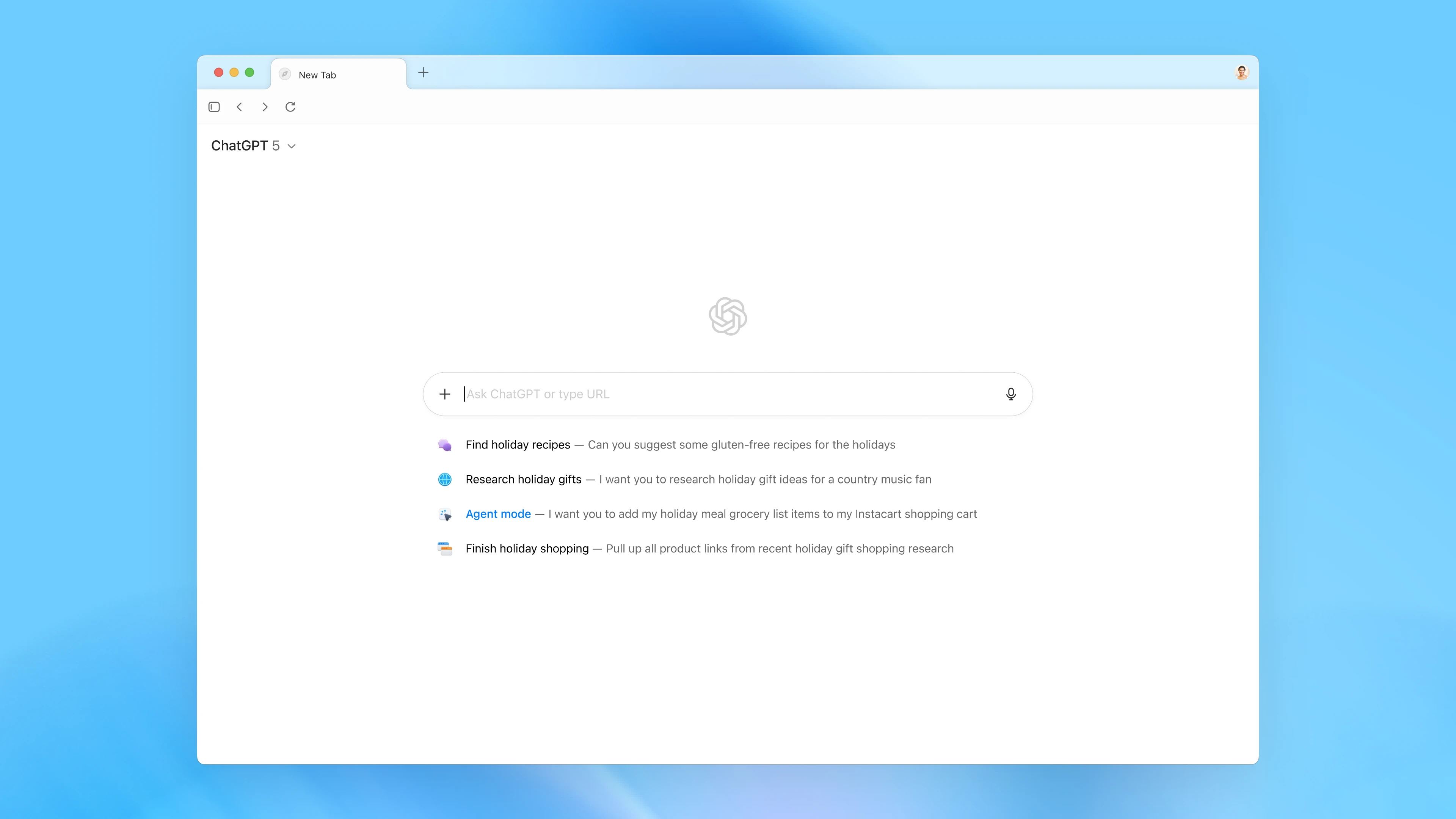
OpenAI has rolled out its latest project, the Atlas web browser, promising a future where most web interactions are facilitated through AI systems. This browser’s robust capabilities include tracking user actions, recalling previous activities, and executing complex tasks autonomously. Currently compatible with macOS, wider support for Windows, iOS, and Android is expected soon.
The concept behind Atlas revolves around integrating browsing directly with ChatGPT, allowing for more versatile and less cluttered user interactions. Its aim is to make the browsing experience feel conversational rather than simply adding AI to existing systems.
According to Ben Goodger, the engineering lead for Atlas, the development began with the idea, “What if you could chat with your browser?” OpenAI seeks to transform browsing by simplifying the complexity of existing systems through conversation.
Atlas aims to distinguish itself from traditional browsers by offering features such as:
- A constant chatbot companion that helps navigate web content.
- Personalized memory that adapts to user preferences over time.
- The ability for ChatGPT to perform tasks on behalf of the user directly through the browser.
The technology promises considerable capabilities, such as managing reservations or editing documents just at the user’s request. Over time, as users engage with Atlas, it will suggest links and tasks that can enhance their browsing experience, from casual news articles to complex trip planning.
Atlas retains familiarity for users with conventional browsing features like tabs and bookmarks, but with added functionalities. An “Ask ChatGPT” button provides instant access to all of ChatGPT’s features, allowing users to summarize content or make edits on the fly while browsing.
The application also utilizes memory, enabling users to recall past interactions, improving the overall browsing experience. Users can make requests in natural language, which Atlas will interpret to reveal relevant pages quickly and efficiently.
However, the integration of AI into web browsing does come with potential concerns regarding privacy and accuracy. OpenAI emphasizes that users should be vigilant about what data they provide and how they manage their interactions with the technology. Data privacy remains a priority, as users have control over their browsing memories.
As OpenAI prepares for broader deployment of the Atlas browser, the potential benefits and risks seem poised to redefine not only how browsing is done but also how technology interacts with everyday life, especially in the context of AI.
